What is Behind ETABS's Simplified C- T- Shear wall Design
- Adisorn O.
- May 14, 2025
- 3 min read
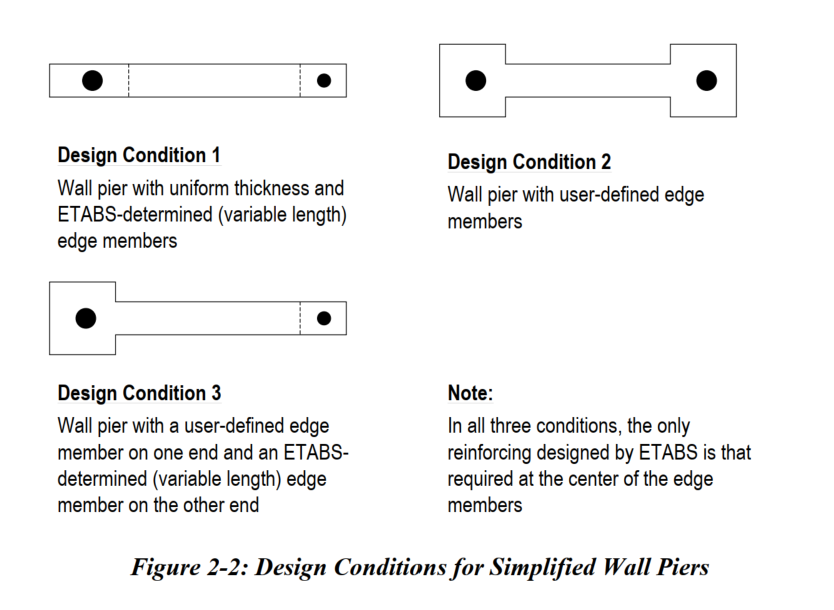
Based on the Shear Wall Design Manual (ACI 318-19), the Simplified C- and T-section shear wall design (Chapter 2.1.1, pages 2-2 to 2-8) involves:
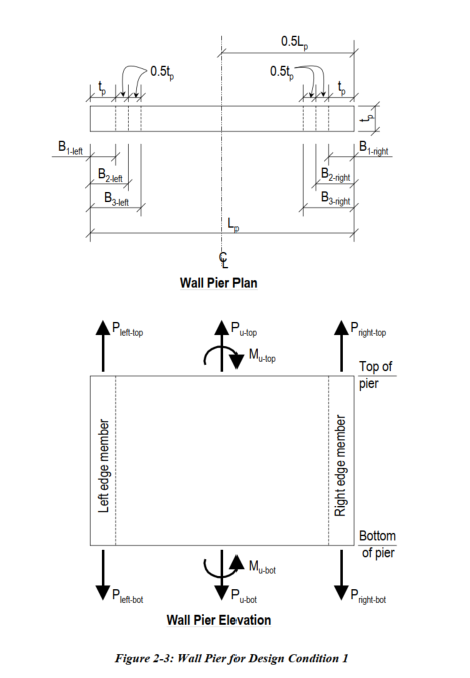
Decomposing the applied axial force (Pu) and moment (Mu) into equivalent axial loads on left and right edge members.
Iteratively sizing the edge member length (B1) until the required steel area (Ast, Asc) is within max allowed ratios (PTmax, PCmax).
Limiting B1 such that B1 ≤ Lp/2.
INPUT:
Pu → axial force on the pier (N or kN)
Mu → moment on the pier (N·mm or kN·m)
Lp → total horizontal length of pier (mm or m)
tp → thickness of wall (mm or m)
fc → concrete strength (MPa)
fy → steel yield strength (MPa)
phi → strength reduction factor
PTmax → max tension steel ratio (e.g., 0.025)
PCmax → max compression steel ratio (e.g., 0.02)
CONVERT all inputs to consistent units (N, mm)
SET:
B1 = tp → initial edge length
max_B1 = Lp / 2 → upper bound per ACI
WHILE B1 <= max_B1:
COMPUTE:
P_left = Pu/2 + Mu / (Lp - B1)
P_right = Pu/2 - Mu / (Lp - B1)
FOR EACH EDGE (left and right):
IF edge axial force < 0 (tension):
Ast = |P| / (phi * fy)
Asc = 0
ELSE (compression):
Ag = B1 * tp
Asc = max( (P - 0.85 * fc * Ag) / (phi * fy), 0 )
Ast = 0
CHECK:
Ast ≤ PTmax * B1 * tp
Asc ≤ PCmax * B1 * tp
IF both edges pass:
REPORT:
Success with current B1
Required Ast and Asc per edge
EXIT
ELSE:
INCREMENT B1 by 0.5 * tp
REPORT:
"Design failed: Steel demand exceeds max allowed even at max B1"
Here's a MATLAB example script that automates this simplified design logic for a planar T-wall section:
MATLAB Sample: Simplified C/T Shear Wall Design
% Given a wall with:
% - Pu = 1500 kN, Mu = 400 kN.m
% - Lp = 4 m, tp = 0.25 m
% - fc = 35 MPa, fy = 500 MPa
% - phi = 0.9, PTmax = 0.025, PCmax = 0.02
design_CT_wall(1500, 5000, 4, 0.25, 35, 500, 0.9, 0.025, 0.02);
function design_CT_wall(Pu, Mu, Lp, tp, fc, fy, phi, PTmax, PCmax)
% Simplified T- or C-wall design: ACI 318-19 based
% Inputs:
% Pu, Mu - factored axial force (N), moment (N.m)
% Lp, tp - wall length (m), thickness (m)
% fc, fy - concrete strength (MPa), steel yield strength (MPa)
% phi - strength reduction factor
% PTmax, PCmax - max steel ratios
% Convert to consistent units (N, mm)
Pu = Pu * 1e3; Mu = Mu * 1e6; % to N and N.mm
Lp = Lp * 1e3; tp = tp * 1e3;
% Start iteration with edge member B1 = tp
B1 = tp;
maxB1 = Lp / 2;
while B1 <= maxB1
% Step 1: Equivalent axial forces at edges
P_left = Pu/2 + Mu / (Lp - B1 );
P_right = Pu/2 - Mu / (Lp - B1);
% Step 2: Design steel areas at both edges
% Initialize steel requirements
Ast_left = 0; Asc_left = 0; Ast_right = 0; Asc_right = 0;
% Left edge
if P_left < 0 % tension
Ast_left = abs(P_left) / (phi * fy ); % mm^2
else % compression
Ag = B1 * tp;
Asc_left = (P_left - 0.85 * fc * Ag) / (phi * fy );
end
% Right edge
if P_right < 0
Ast_right = abs(P_right) / (phi * fy );
else
Ag = B1 * tp;
Asc_right = (P_right - 0.85 * fc * Ag) / (phi * fy );
end
Asc_left = max(0, Asc_left);
Asc_right = max(0, Asc_right);
% Step 3: Check against max ratios
Ast_max = PTmax * B1 * tp;
Asc_max = PCmax * B1 * tp;
if Ast_left <= Ast_max && Asc_left <= Asc_max && ...
Ast_right <= Ast_max && Asc_right <= Asc_max
fprintf('\n=== Final Design ===\n');
fprintf('Edge Member Width (B1): %.1f mm\n', B1);
fprintf('Left Edge: Ast = %.1f mm², Asc = %.1f mm²\n', Ast_left, Asc_left);
fprintf('Right Edge: Ast = %.1f mm², Asc = %.1f mm²\n', Ast_right, Asc_right);
return
end
% Increment B1
B1 = B1 + 0.5 * tp;
end
disp('Design failed: Required reinforcement exceeds limit even at max edge width.');
end
Output Explanation:
It iteratively increases the edge leg size B1 (starting from tp) until reinforcement demands are within limits.
Computes and prints required tension (Ast) and compression (Asc) areas at each edge.


